Itchy ears are usually a sign of infection, more of a fungal nature. Ear infections are mainly of two kinds viz; fungal and bacterial. Fungal infections are usually termed as Otomycosis (oto=ear, mycosis=fungi).
These infections are caused by mainly two kinds of fungi namely Aspergillus and Candida. The incidence being 10% of all ear canal infections (otitis externa), it is found to be more prevalent in hot and subtropical climates, which peaked during summer months with higher chances in those indulging in aquatic sports. That probably may be the reason why it is also called as Swimmer’s ear.
Cerumen or ear wax (pH 4-5) keeps bacteria and fungi away from the external auditory canal when secreted in normal amounts. During aquatic sports and swimming, the cerumen gets washed away, resulting in dryness of the canal inviting external microorganisms creating infections. Other reasons are local trauma commonly caused by ear buds and cotton swabs, increased temperature, high humidity, eczema etc.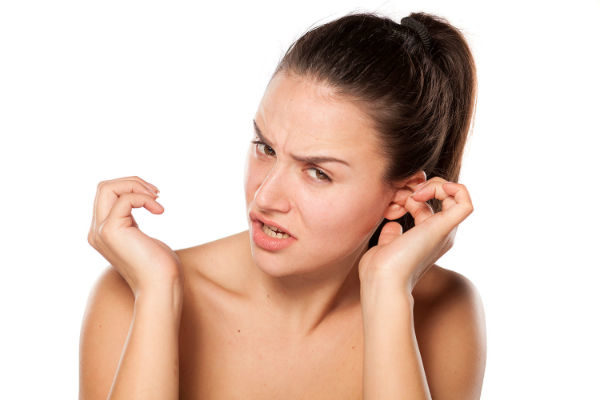
Otitis externa is the inflammation of the external auditory canal, mostly due to infection or allergy. Bacterial invasion usually results in similar condition associated with other symptoms. Your shampoo, hairspray or even water drops that enter your ears may turn problematic if you are prone to infections. This makes you itch your ears, causing injury to your external ear canal which in turn invites further infection. Other reasons include trauma, fungal infection, sweaty weather, eczema, psoriasis, or swimming.
Presentation may include inflammation, pruritis, scaling and severe discomfort. Superficial exfoliation and debris containing hyphae along with suppuration is also seen in case of fungal infections whereas painful discharging ears are of bacterial origin. A differential diagnosis may be made probably when you fail to respond to antibiotics. It is also possible that topical antibiotics have predisposed to fungal infection.
Management of ear infections, or lets say any infection may not always necessarily be of topical or oral origin. Ayurveda has opened a wide range of antimicrobial anti-infective agents which would help smoke away the causative organisms, which means a course of internal administration of medicine may not always be necessary. These antimicrobial drugs, when burnt produce medicinal smoke that destroys harmful microorganisms. This holds good in not just ear infections but almost everywhere when you need the area to be sterilized. This method of using medicinal smoke is called Dhoopana and particularly karnadhoopana when the area to be treated is ears. Here are a few commonly seen drugs that are effective for Dhoopana:
1, Guggulu (Botanical name: Comiphora mukul Family: Burseraceae)
This drug is widely used in preparation of Ayurvedic medicines owing to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties. It produces a gum resin like substance which is further purified and used for medicinal purpose.
2, Agaru (Botanical name: Aquillaria agallocha Family: Thymellaceae)
 A black coloured bark, used in Ayurvedic pharmaceutics. It is a tropical and subtropical fragrant evergreen tree. The wood is very heavy and sinks in water. Its wood pieces are available with no characteristic smell or odour.
A black coloured bark, used in Ayurvedic pharmaceutics. It is a tropical and subtropical fragrant evergreen tree. The wood is very heavy and sinks in water. Its wood pieces are available with no characteristic smell or odour.
3, Neem (Botanical name: Azadirachta indica Family: Meliaceae)
 It is native to india, Myanmar, Srilanka, etc. it is a versatile plant which has suprising effects on skin, eye disorders, intestinal worms, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, against cancer and bacteria. It is also used in Yogic sadhana and is a part of culture and tradition of Indian rituals.
It is native to india, Myanmar, Srilanka, etc. it is a versatile plant which has suprising effects on skin, eye disorders, intestinal worms, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, against cancer and bacteria. It is also used in Yogic sadhana and is a part of culture and tradition of Indian rituals.
4, Turmeric (Botanical name: Curcuma longa Family: Zingiberaceae)
 It is a rhizomatous herb possessing bioactive compounds with powerful medicinal properties like anti-inflammatory, anti-infective and anticancer effects. It dramatically increases the antioxidant capacity of the body, improves brain function, prevents Alzheimer’s disease and has incredible effects against mental depression.
It is a rhizomatous herb possessing bioactive compounds with powerful medicinal properties like anti-inflammatory, anti-infective and anticancer effects. It dramatically increases the antioxidant capacity of the body, improves brain function, prevents Alzheimer’s disease and has incredible effects against mental depression.
5, Vacha (Botanical name: Acorus calamus Family: Zingiberaceae)
 It is a commonly used drug in Ayurveda, right from neonatal care due to its ability to produce lucidity in mind. It is a promising brain tonic, promotes higher mental functions, increases alertness and focus. It reduces mucus and digestive gas throughout the body.
It is a commonly used drug in Ayurveda, right from neonatal care due to its ability to produce lucidity in mind. It is a promising brain tonic, promotes higher mental functions, increases alertness and focus. It reduces mucus and digestive gas throughout the body.